Implementing Digital Signatures in Java
Introduction
In today's digital age, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of electronic documents is crucial. Digital signatures offer a robust solution to this problem, providing a way to verify the origin and integrity of data. In this blog post, we'll explore how to implement digital signatures in Java, leveraging the powerful cryptographic libraries available in the Java ecosystem.
What is a Digital Signature?
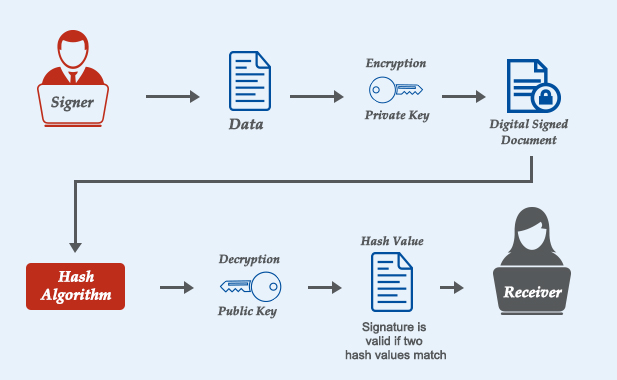
A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message, software, or digital document. It provides assurances that the message was created by a known sender (authentication) and that it was not altered in transit (integrity).
Key Concepts
Before diving into the implementation, let's briefly cover the key concepts involved in digital signatures:
Hash Function: A function that converts an input (or 'message') into a fixed-length string of bytes. The output is unique to each unique input.
Private Key: A secret key used to create the digital signature.
Public Key: A public key used to verify the digital signature.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have Java Development Kit (JDK) installed on your machine. We'll be using Java's built-in libraries for cryptographic operations.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Generate Key Pair
First, we need to generate a public-private key pair. Java provides the KeyPairGenerator class to facilitate this.
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static KeyPair generateKeyPair() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGen.initialize(2048);
return keyPairGen.generateKeyPair();
}
}
Step 2: Create a Digital Signature
Now that we have our key pair, we can create a digital signature. We'll use the Signature class to sign data using our private key.
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.Signature;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static byte[] signData(byte[] data, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.sign();
}
}
Step 3: Verify the Digital Signature
To verify the signature, we'll use the corresponding public key.
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.Signature;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static boolean verifySignature(byte[] data, byte[] signatureBytes, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.verify(signatureBytes);
}
}
Step 4: Putting It All Together
Let's combine the above steps into a single application to demonstrate the complete process.
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.Signature;
public class DigitalSignatureApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Generate key pair
KeyPairGenerator keyGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyGen.initialize(2048);
KeyPair pair = keyGen.generateKeyPair();
PrivateKey privateKey = pair.getPrivate();
PublicKey publicKey = pair.getPublic();
// Data to be signed
String data = "This is a secret message";
byte[] dataBytes = data.getBytes();
// Sign the data
byte[] signature = signData(dataBytes, privateKey);
System.out.println("Digital Signature: " + new String(signature));
// Verify the signature
boolean isVerified = verifySignature(dataBytes, signature, publicKey);
System.out.println("Signature Verified: " + isVerified);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static byte[] signData(byte[] data, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.sign();
}
public static boolean verifySignature(byte[] data, byte[] signatureBytes, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.verify(signatureBytes);
}
}
Conclusion
In this post, we've covered the basics of digital signatures and demonstrated how to implement them in Java. By generating a key pair, signing data with a private key, and verifying the signature with a public key, you can ensure the integrity and authenticity of your digital communications. Digital signatures are a powerful tool for securing data in a wide range of applications, from email to software distribution